Molecular therapies for cancer represent a groundbreaking frontier in the ongoing battle against malignant diseases, offering targeted solutions that address the roots of uncontrollable growth. As innovative cancer treatment innovations emerge, researchers delve into the complexities of oncogenic processes, utilizing advanced strategies such as molecular glues to alter protein interactions within cancer cells. Recent studies led by Harvard’s Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology have showcased the power of small molecules to disrupt critical protein networks, paving the way for effective therapies that were once considered unattainable. By understanding how specific genetic mutations mimic the action of these molecular glues, scientists are carving a path towards precision medicine that could revolutionize cancer care. The integration of targeted therapies underscores a new era in oncology, where personalized approaches become possible through detailed insights into molecular mechanisms.
In the realm of cancer treatment, the emergence of molecular-based therapies marks a significant advancement in oncology. These cutting-edge strategies, often described as targeted treatments, aim to intervene at the molecular level by manipulating aberrant protein interactions responsible for tumor development. Researchers are now exploring the potential of small molecules, commonly referred to as molecular glues, which can effectively disrupt oncogenic signaling pathways. Such breakthroughs are not only enhancing our understanding of cancer biology but also providing new avenues for therapeutic interventions tailored to individual patients. By leveraging insights into genetic mutations and their effects on protein networks, a new paradigm of cancer management is being established.
Advancements in Molecular Therapies for Cancer
Recent breakthroughs in molecular therapies for cancer have opened new avenues for combating various cancer types. Researchers at Harvard have developed small molecules that can effectively target critical protein interactions involved in cancer growth. By manipulating these interactions, scientists aim to disrupt the harmful processes that lead to cancer progression. These innovative approaches not only hold great promise for improving cancer treatment but also pave the way for better understanding of oncogenic processes at the molecular level.
The findings from recent studies, particularly on molecular glues, demonstrate a fascinating convergence of genetic mutations and chemical interventions. This dual approach allows for a more refined targeting of cancerous cells, highlighting the importance of molecular therapies in the contemporary landscape of cancer treatment. As the body of research expands, the potential for creating therapies that can intelligently target proteins involved in cancer is becoming increasingly feasible.
Understanding Molecular Glues in Cancer Treatment Innovations
Molecular glues represent a noteworthy innovation in the field of cancer treatment. These small molecules function by binding two proteins together that normally do not interact, facilitating a cascade of biological events that lead to the degradation of one of the proteins involved in tumor growth. The research team’s focus on the molecule UM171 revealed its ability to degrade the CoREST complex, which is crucial for gene regulation and is often implicated in cancer. Such mechanisms reveal how molecular glues can target previously undruggable proteins, which is a major leap forward in cancer treatment innovations.
Moreover, understanding how molecular glues can alter vital protein interaction networks helps to clarify the complex relationships within cancerous cells. By using multidisciplinary approaches, including structural biology and functional genomics, researchers can visualize these interactions in action. This understanding not only aids in the design of robust therapies but also informs ongoing research into the various roles that protein interactions play in oncogenic processes, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of cancer biology.
The Role of Targeted Therapies in Oncology
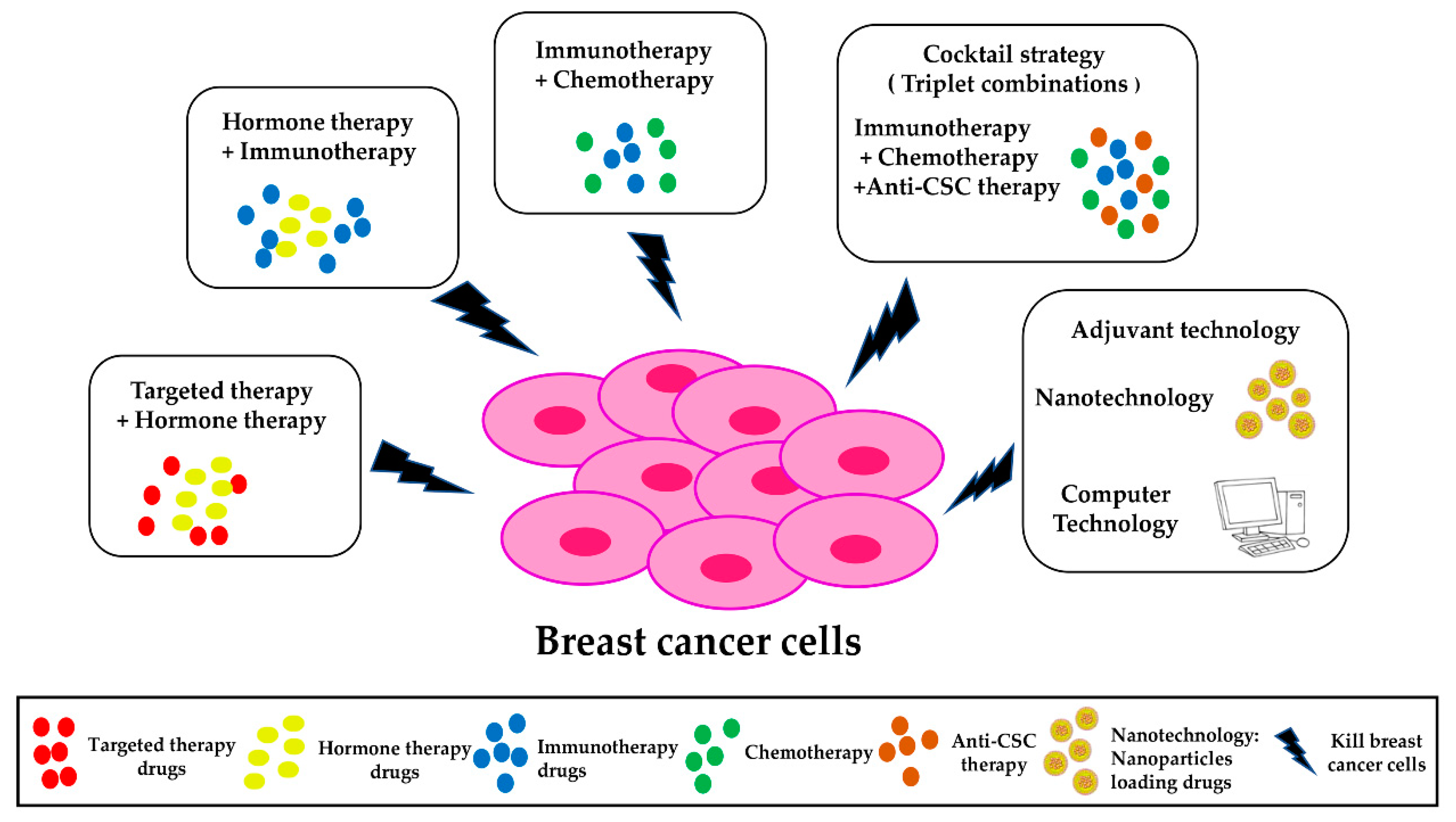
Targeted therapies are revolutionizing oncology by providing more personalized treatment options. These therapies are designed to specifically disrupt the molecular mechanisms involved in cancer cell growth and survival, resulting in enhanced treatment efficacy with potentially reduced side effects. The recent studies on molecular glues exemplify how targeted therapies can be developed to respond to specific oncogenic mutations, thus increasing the likelihood of successful outcomes for patients with various forms of cancer.
In conjunction with molecular therapies, the development of targeted therapies has driven forward the understanding of cancer at both a molecular and genetic level. With tools like cryo-electron microscopy, researchers can visualize the effects of specific mutations on protein behavior, allowing for targeted interventions. This synergy between targeted mechanisms and molecular therapy development underscores the importance of a multidisciplinary approach in the fight against cancer.
Insights into Oncogenic Processes Through Research
A deeper understanding of oncogenic processes is essential for the development of effective cancer therapies. The studies conducted by the Harvard research team highlight the intricate relationships between genetic mutations and cancer cell behavior. By identifying and characterizing the effects of these mutations on protein interactions, researchers can more clearly delineate how cancer cells manage to proliferate uncontrollably.
This insight into the oncogenic landscape lays the groundwork for creating therapies that specifically target these processes. By disrupting the molecular underpinnings of cancer, such as through the application of molecular glues and targeted therapies, researchers can shift the paradigm of traditional cancer treatment, moving towards more precise and effective strategies.
Exploring Protein Interactions in Cancer Therapy
Protein interactions play a crucial role in the cellular processes that lead to cancer. The ability to understand and manipulate these interactions opens new dimensions in cancer therapy. The molecular glues studied by the Harvard team illustrate how specific binding events can initiate pathways leading to protein degradation, effectively reducing the levels of oncogenic proteins in cancer cells.
Exploring these protein interactions allows researchers to identify potential targets for therapeutic intervention. By leveraging knowledge about how proteins normally interact and how this can be altered by molecular glues, scientists can devise new treatments aimed at specific cellular pathways, enhancing the precision and impact of cancer therapies.
The Future of Molecular Strategies in Cancer Research
The future of molecular strategies in cancer research is promising, with ongoing efforts to uncover additional protein interactions and oncogenic mutations. Researchers like Brian Liau emphasize the importance of integrating genetic and chemical approaches to discover novel molecular glues and therapies. The continual exploration of how molecular interventions can reshape oncogenic processes is imperative for the future landscape of cancer treatment.
As scientists advance their understanding of the complex interactions within cancer cells, they are likely to develop increasingly sophisticated treatments. The potential to transition from traditional approaches to innovative molecular therapies is transforming cancer care, suggesting an exciting future for both researchers and patients alike.
Challenges in Developing Molecular Therapies for Cancer
Despite the promising advancements in molecular therapies for cancer, several challenges remain in their development and application. The complexity of protein interactions can make it difficult to design effective therapies that selectively target cancer cells without affecting healthy tissues. Additionally, the identification of suitable molecular glues can be a daunting task due to the variety of oncogenic mutations involved.
Another challenge lies in translating research findings into clinical applications. While laboratory studies may demonstrate the effectiveness of molecular therapies, ensuring their safety and efficacy in humans is a critical hurdle that must be overcome. Addressing these challenges through collaborative research and advancements in technology will be vital for the successful implementation of molecular therapies in cancer treatment.
The Significance of Genetic Mutations in Cancer
Genetic mutations serve as significant contributors to cancer development and progression. Understanding which mutations lead to aberrant biochemical pathways is vital for creating tailored therapeutic strategies. The research focused on KBTBD4 mutations illuminates how specific genetic alterations can shift protein interactions, resulting in disrupted cellular functions and promoting oncogenesis.
This emphasis on genetic mutations allows for the development of personalized therapies that target the specific changes within a patient’s cancer cells. By leveraging knowledge about the genetic profile of tumors, clinicians can apply targeted therapies that are more likely to succeed, thereby improving treatment outcomes and potentially reducing the risk of resistance.
Collaborative Efforts Across Research Institutions
Collaboration among various research institutions is a cornerstone of significant progress in cancer therapy development. The collective expertise brought together by teams from Harvard Medical School, the Broad Institute, and other institutions has enabled comprehensive studies that integrate various scientific disciplines. This interdisciplinary approach is essential in deciphering complex oncogenic mechanisms and developing novel molecular therapies.
The power of these collaborative efforts lies in their ability to pool resources and knowledge, fostering an environment conducive to innovation. As researchers come together across disciplines, the advancements in understanding cancer biology and the development of effective therapies will continue to flourish.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are molecular therapies for cancer and how do they work?
Molecular therapies for cancer involve innovative treatments that target specific molecular mechanisms of cancer cells. These therapies aim to disrupt oncogenic processes by interfering with protein interactions or using small molecules, known as molecular glues, to promote the degradation of cancer-causing proteins. Such approaches enhance precision in cancer treatment by addressing unique genetic mutations and cellular pathways inherent in different types of cancer.
How do targeted therapies differ from traditional cancer treatments?
Targeted therapies differ from traditional cancer treatments by focusing on specific molecular targets associated with cancer cells, rather than indiscriminately killing all rapidly dividing cells. This allows for potentially fewer side effects and increased efficacy. By exploiting unique features of cancer cells, such as specific mutations or protein interactions, targeted therapies can effectively disrupt the growth and spread of cancer.
What role do molecular glues play in cancer treatment innovations?
Molecular glues are small molecules that facilitate the interaction between proteins that normally do not bind together. In cancer treatment innovations, these molecules can activate a cell’s degradation pathways to eliminate unwanted oncogenic proteins. By targeting proteins traditionally considered undruggable, molecular glues represent a significant advancement in designing effective cancer therapies.
Can molecular therapies for cancer address genetic mutations?
Yes, molecular therapies for cancer are designed to address specific genetic mutations within cancer cells. By understanding how these mutations affect protein interactions and function, researchers can develop targeted therapies that specifically disrupt aberrant pathways, ultimately leading to more effective treatment options tailored to individual genetic profiles.
What challenges exist in developing molecular therapies for cancer?
Developing molecular therapies for cancer presents several challenges, including identifying and validating new molecular targets, understanding complex protein interactions, and ensuring the therapies effectively penetrate cancer cells. Additionally, researchers must overcome the difficulty of designing drugs that can selectively target only the cancerous proteins without affecting normal cellular functions.
How do oncogenic processes influence the design of molecular therapies?
Oncogenic processes significantly influence the design of molecular therapies by highlighting key alterations in signaling pathways, mutations, and cellular mechanics that drive cancer growth. By studying these processes, researchers can discover unique molecular targets and design therapies, such as molecular glues, that specifically disrupt the cancer-promoting interactions, leading to more effective treatment strategies.
What is the importance of studying protein interactions in molecular therapies for cancer?
Studying protein interactions is crucial in molecular therapies for cancer as these interactions often dictate cellular processes, including growth and survival. Understanding how proteins interact allows researchers to identify potential therapeutic targets and design strategies to disrupt harmful interactions, thereby providing a pathway for developing more precise and effective cancer treatments.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Advancement in Molecular Therapies | Research by Harvard scientists introduces innovative molecular therapies that target cancer at a molecular level. |
| Molecular Glues | Molecular glues are small molecules that bind otherwise incompatible proteins to activate degradation systems in cells. |
| Targeted Protein Interactions | The studies demonstrate how molecular glues can target proteins previously considered ‘undruggable’, like the CoREST complex. |
| Genetic Mutations in Cancer | The research reveals how specific mutations in proteins, such as KBTBD4, can lead to aberrant cancer processes. |
| New Research Paradigms | Utilizing both molecular and genetic approaches provides a new framework for cancer therapy development. |
Summary
Molecular therapies for cancer represent a groundbreaking shift in treating malignancies by targeting the disease at its molecular roots. The recent studies by Harvard scientists have illustrated the potential of molecular glues and genetic mutations in controlling cancer cell growth, offering insights that could redefine therapeutic strategies against various cancers. By examining the intricate dynamics between small molecules and genetic modifications, researchers are paving the way towards more effective and targeted treatment options, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes.