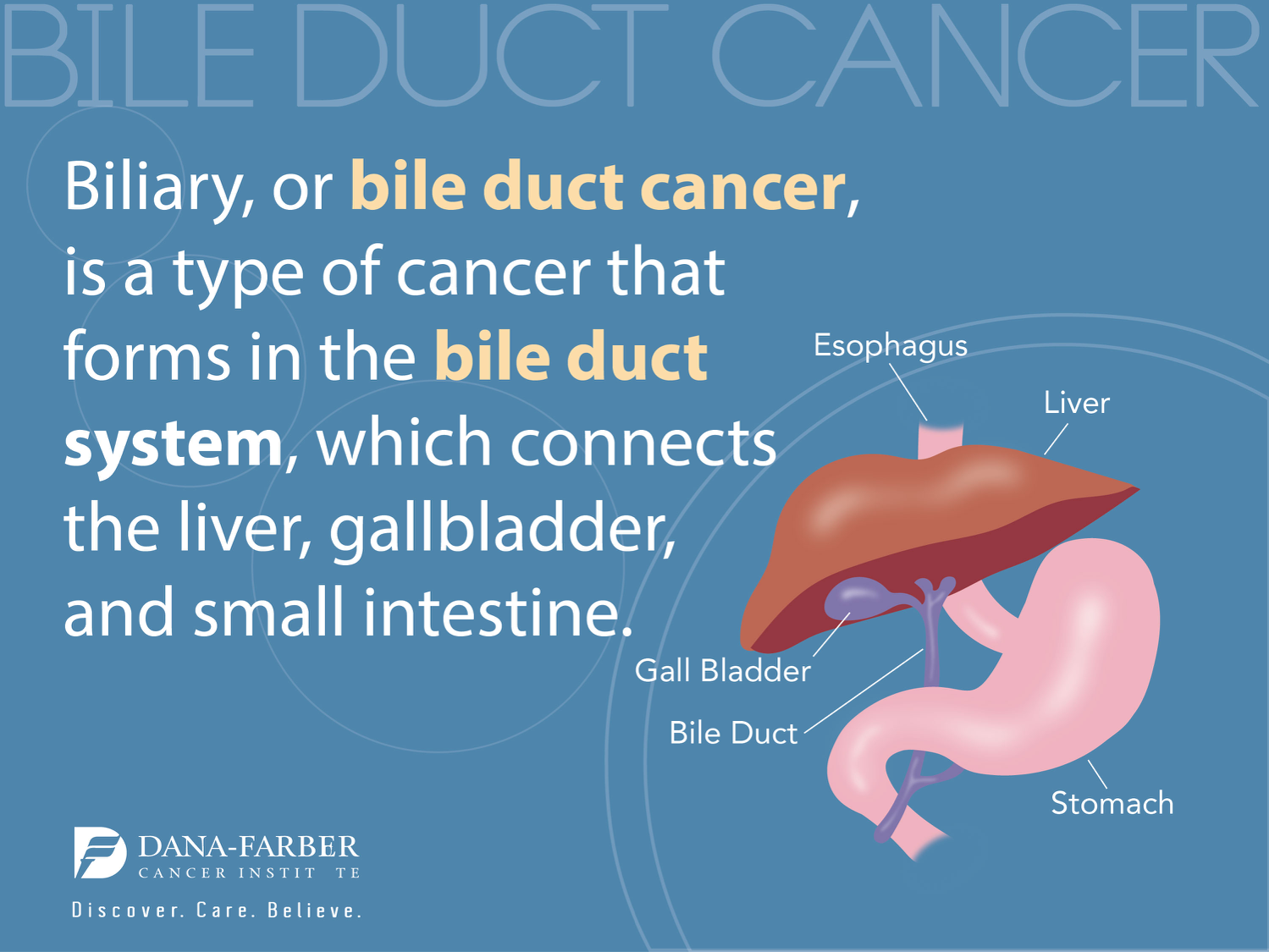
Bile imbalance liver cancer is emerging as a significant health concern, particularly due to its link with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent type of liver cancer. Recent research highlights how disruptions in bile acid production can lead to the development of this aggressive malignancy. Bile acids, essential for fat digestion, also regulate crucial metabolic processes, making their balanced production vital for liver health. The study identifies the FXR receptor as pivotal in maintaining bile homeostasis, suggesting that its dysfunction may promote cancer progression. With this newfound understanding, potential liver cancer treatments may focus on correcting bile imbalances and targeting the YAP protein role, offering hope for effective interventions.
The connection between bile acid dysregulation and liver cancer has garnered attention in the medical community, especially when discussing conditions like hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Bile, produced by the liver, plays a crucial role not only in digestion but also in metabolic regulation. As researchers delve deeper into the molecular processes, they discover pathways like the FXR receptor’s influence on bile secretion and how imbalances can trigger liver damage. Understanding the role of proteins such as YAP in this context may offer new avenues for pharmacological interventions. By addressing bile acid-related issues, there is potential to transform liver cancer treatments and improve patient outcomes.
Understanding Bile Imbalance and Its Impact on Liver Cancer
A bile imbalance is increasingly recognized as a key factor in the development of liver diseases, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the predominant type of liver cancer. This imbalance occurs when there is an overproduction of bile acids, which is detrimental to liver health and can lead to severe complications, including inflammation and fibrosis. Recent research has illuminated the molecular mechanisms underlying this phenomenon, emphasizing the role of the FXR receptor, a critical bile acid sensor. When the function of FXR is compromised, bile acids accumulate, resulting in a cascade of pathological events that can precede liver cancer.
Specifically, the research indicates that the YAP protein plays a pivotal role in regulating bile acid metabolism. By inhibiting FXR, YAP inadvertently contributes to the bile imbalance that characterizes liver cancer progression. Understanding this interplay opens new avenues for therapeutic interventions. Developing treatments that target YAP’s repressive function or enhance the activity of FXR can provide potential strategies to restore bile acid homeostasis and mitigate liver cancer risk.
The Role of FXR in Liver Cancer Treatments
The Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) is emerging as a central player in the treatment of liver cancer through its regulatory role in bile acid homeostasis. FXR helps to control the synthesis and excretion of bile acids, ensuring that levels remain within a healthy range. When FXR is activated, it can alleviate the overproduction of bile acids that leads to liver damage and inflammation — precursor conditions for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Pharmacological agents that stimulate FXR signaling could thus hold promise in both preventing and treating bile imbalance-related liver cancers.
Recent studies have shown that agents enhancing FXR activity can decrease liver fibrosis and slow cancer progression. This offers a dual benefit: not only do these treatments restore normal bile acid levels, but they also promote cellular health within the liver. Furthermore, by employing innovative approaches to target FXR, researchers aim to develop safe and effective treatment protocols that could revolutionize care for patients at risk of or currently battling liver cancer.
Deciphering the YAP Protein’s Role in Liver Health
YAP (Yes-associated protein) is a crucial element in the development of liver cancer, specifically due to its unexpected role in bile acid metabolism. Initially thought to drive cell proliferation, recent findings highlight its function as a repressor of FXR activity. This dual role complicates the understanding of YAP’s contribution to liver health. When YAP inhibits FXR, bile acids accumulate, leading to cellular stress and inflammation, which significantly increases the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma.
Targeting YAP presents a unique strategy for liver cancer intervention. By modulating YAP activity, scientists are exploring ways to restore FXR function, which could minimize bile acid toxicity in the liver. Researchers are optimistic that by manipulating the YAP signaling pathway, they can develop new therapeutic avenues to counteract bile imbalance and its dire consequences in liver cancer.
Strategies to Enhance Bile Acid Clearance
One of the promising strategies for mitigating liver cancer risk associated with bile imbalance is enhancing the clearance of bile acids from the liver. This can be accomplished through the development of drugs that promote the expression of bile acid export proteins, such as BSEP (Bile Salt Export Pump). By increasing the efflux of bile acids, these therapies aim to reduce hepatic accumulation and restore balance, thereby protecting against inflammation and fibrosis that often lead to hepatocellular carcinoma.
Moreover, integrating lifestyle modifications along with pharmaceutical interventions could significantly improve bile acid dynamics. A diet rich in fiber has been noted to promote healthy bile acid metabolism and enhance gut health, which in turn supports liver function. The combination of these strategies may not only prevent bile imbalance but also serve as a holistic approach to liver cancer prevention and treatment.
Exploring Innovative Treatments for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Recent breakthroughs in molecular biology have ushered in a new era for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). As research unveils the complex interplay between bile acid metabolism and cancer development, targeted therapies that address the underlying causes of bile imbalance are garnering attention. Agents that enhance the function of the FXR receptor or inhibit the repressive action of YAP are at the forefront of this innovative treatment landscape.
Additionally, combination therapies that incorporate existing treatments with new agents targeting bile acid homeostasis could prove to be effective. As we refine our understanding of how bile acids influence liver cancer progression, the integration of these findings into clinical practice could lead to improved outcomes for patients suffering from liver cancer.
The Relationship Between Inflammation and Liver Cancer
Chronic inflammation is a well-established risk factor for liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The accumulation of bile acids due to hepatic dysfunction can incite a robust inflammatory response, further perpetuating liver damage and increasing the likelihood of cancer development. Understanding this relationship is crucial for developing preventative strategies that can mitigate inflammation-related liver cancer risks.
By leveraging insights into bile acid metabolism and its impact on inflammation, researchers are actively investigating therapeutic agents that not only target bile homeostasis but also possess anti-inflammatory properties. This multifaceted approach aims to address both the causes and consequences of liver disease, ultimately improving patient outcomes in the fight against liver cancer.
Advancements in Liver Cancer Research and Drug Development
The field of liver cancer research is rapidly evolving, with significant advancements in understanding the molecular mechanisms that govern diseases such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Cutting-edge studies are providing insights into how various pathways, particularly those involving bile acids, FXR, and YAP, contribute to liver cancer pathology. These discoveries are paving the way for innovative drug development that targets the critical players involved in bile imbalance.
Furthermore, collaboration among researchers, clinicians, and pharmaceutical companies is crucial in translating scientific findings into viable therapeutic options. With ongoing research into bile acid signaling and liver health, the potential for new treatments aimed specifically at correcting bile imbalance and preventing liver cancer becomes more tangible, offering hope to patients at risk of this devastating disease.
The Importance of Early Detection in Liver Cancer
Timely detection of liver cancer remains a vital aspect of improving survival outcomes, especially in cases linked to underlying conditions such as bile imbalance. Understanding the signs and symptoms associated with liver dysfunction can empower individuals to seek medical attention early. Regular monitoring of liver health in individuals at high risk, such as those with chronic liver diseases, is essential for early diagnosis of conditions that may precipitate hepatocellular carcinoma.
Innovative screening methods, including imaging techniques and biomarkers related to bile acid metabolism, are under investigation to enhance early detection. These advancements aim to identify liver cancer at its nascent stages, allowing for interventions that can halt disease progression and significantly improve prognosis.
Lifestyle Measures to Reduce Liver Cancer Risk
In addition to medical interventions, lifestyle choices play a critical role in reducing the risk of liver cancer associated with bile imbalance. Adopting a balanced diet, rich in antioxidants and fiber, can promote healthy liver function and support optimal bile acid metabolism. Limiting alcohol intake and avoiding high-calorie processed foods are also important measures that contribute to overall liver health.
Furthermore, regular physical activity has been linked to improved liver health as it helps maintain a healthy weight and enhances metabolic processes, including bile acid regulation. Integrating these lifestyle measures with medical advancements in therapy could significantly decrease the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma and improve quality of life for individuals at risk.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the relationship between bile imbalance and liver cancer?
Bile imbalance is linked to liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Disruptions in bile acid production can lead to liver inflammation and injury, setting the stage for cancer development. Research indicates that an overproduction of bile acids may induce fibrosis and contributes to the progression of liver cancer.
How do bile acids influence liver cancer treatments?
Bile acids play a crucial role in liver cancer treatments by affecting molecular pathways involved in cancer progression. Enhancing the function of the Farnesoid X receptor (FXR), which is vital for bile acid regulation, could be a promising therapeutic strategy. Targeting these pathways may help mitigate tumor formation linked to bile imbalances.
What role does the YAP protein play in bile acid metabolism and liver cancer?
The YAP protein is involved in regulating bile acid metabolism. In liver cancer, YAP acts as a repressor that hinders FXR function, leading to excess bile acid production. This imbalance can escalate inflammation and liver damage, contributing to the development of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Can targeting the FXR receptor improve outcomes for liver cancer patients?
Yes, targeting the FXR receptor presents a potential strategy for improving outcomes in liver cancer patients. Enhancing FXR function can restore bile acid homeostasis, reduce inflammation, and ultimately limit the progression of liver cancer associated with bile imbalances.
What are the implications of blocking YAP’s repressor activity in liver cancer treatment?
Blocking YAP’s repressor activity may hold significant implications for liver cancer treatment. By improving FXR function or promoting bile acid excretion, researchers aim to disrupt the cycle that leads to liver fibrosis and cancer, potentially opening avenues for pharmacological interventions against hepatocellular carcinoma.
How does the Hippo/YAP pathway influence liver cancer risk?
The Hippo/YAP pathway plays a critical role in regulating cell growth and metabolism in the liver. Dysregulation of this pathway, especially through the action of YAP, can affect bile acid metabolism and contribute to liver injury and increased cancer risk, particularly in the context of hepatocellular carcinoma.
What are potential research directions stemming from the findings on bile imbalance and liver cancer?
Future research may focus on developing pharmacological strategies that stimulate FXR to restore bile acid balance and investigating the broader metabolic impacts of YAP on liver health. Understanding these mechanisms can lead to innovative treatment approaches for liver cancer linked to bile imbalances.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance | An imbalance in bile acids can lead to progression of liver diseases, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). |
| Molecular Switch | A study identified a key molecular switch, YAP, that affects bile acid metabolism, leading to liver cancer. |
| YAP’s Role | YAP promotes tumor formation while impairing the bile acid sensor FXR, causing bile acid overproduction. |
| Potential Treatments | Strategies include enhancing FXR function, blocking YAP’s repressor activity, and promoting bile acid excretion to combat liver damage. |
Summary
Bile imbalance liver cancer is a critical health concern linked to the disruption of bile acid metabolism, which is essential for proper digestion and metabolic regulation. A recent study highlights the connection between bile acid imbalance and the development of liver cancer, emphasizing the role of the YAP protein in this process. By targeting YAP and enhancing bile acid regulation, researchers aim to develop effective therapeutic strategies to combat liver cancer and improve patient outcomes.