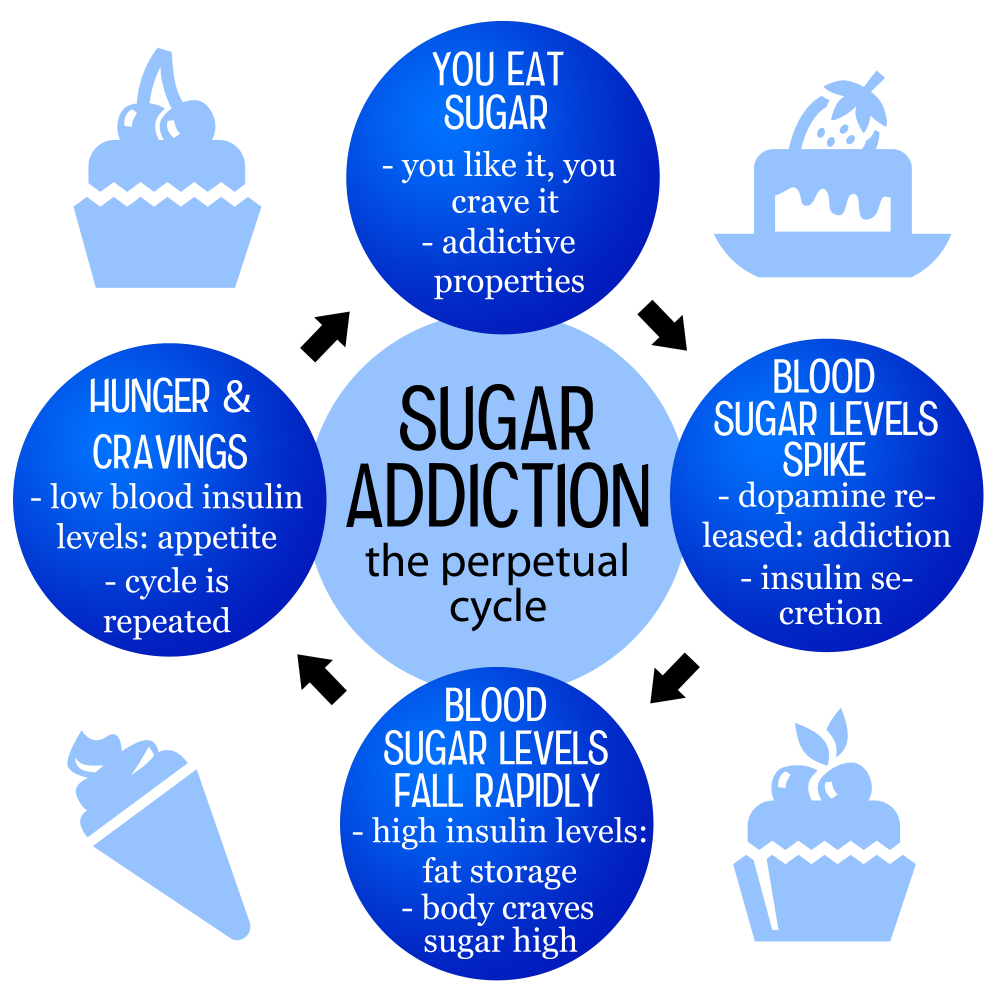
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked heated debates among nutrition researchers and health advocates alike. While substances like alcohol and nicotine are recognized as addictive due to their powerful effects on the brain, sugar presents a more complex case. Although it can trigger sugar cravings and foster habitual consumption, many argue that it does not meet the clinical criteria for addiction. The effects of sugar, particularly added sugar consumption found in ultra-processed foods, can lead to heightened cravings and negative health consequences when overindulged. As we explore the topic of sugar addiction, it’s essential to understand both its psychological and physiological impacts on our lives.
When discussing the potential for sugar to be classified as an addiction, various terms come into play. The notion of sugar dependence reflects how some individuals may feel compelled to consume sweets beyond mere preference, experiencing a form of withdrawal when attempting to decrease intake. Alternative phrases like “sugar cravings” and “sweet substance compulsions” further emphasize the behavioral patterns that can arise from the overconsumption of this ubiquitous ingredient. The dialogue around excessive sugar in our diets often intersects with broader discussions on nutrition, where the effects of sugar on the body can mirror some addictive behaviors seen with more traditionally recognized substances. By examining these connections, we deepen our understanding of our relationship with sugar and its diverse roles in our dietary choices.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
Sugar addiction is a widely debated topic among nutrition experts. While many people report experiencing cravings similar to those triggered by addictive substances like nicotine and alcohol, the classification of sugar as an addictive substance remains contentious. Several studies indicate that sugar can induce cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, leading to a dependency-like state in some individuals. This propensity for craving sugary foods is notably intensified by the prevalence of ultra-processed foods that are high in added sugars and other unhealthy ingredients. The accessibility and palatability of these products can foster habitual consumption patterns that resemble addiction.
Despite the physical and psychological responses associated with sugar consumption, official clinical guidelines do not categorize sugar as an addictive substance. This distinction is critical as it highlights the inherent differences between sugar and more harmful substances like alcohol or opioids. While individuals may experience withdrawal-like symptoms such as anxiety and headaches when reducing sugar intake, these symptoms are often less severe compared to those associated with more traditional addictions. Understanding the nuances surrounding sugar addiction can help individuals foster a healthier relationship with their diets and make informed choices about their consumption.
The Psychological Effects of Sugar Consumption
The psychological effects of consuming high amounts of sugar can be profound. As indicated by nutrition researchers, the effects of sugar on mood and behavior are significant and can mirror the psychological impact seen in addiction to more severe substances. For instance, the rush of pleasure that follows the consumption of sugary foods can lead to repeated cravings, creating a cycle whereby individuals seek out that pleasurable feeling more frequently. This not only leads to increased sugar consumption but also heightens the risk of developing unhealthy eating habits.
Moreover, the frequent availability of processed foods loaded with added sugars keeps the temptation alive, making it challenging for individuals to cut back. People often find themselves in a complicated relationship with sugar, where they crave it and may feel guilty afterward, leading to emotional eating. Recognizing these psychological effects is vital for understanding how sugar cravings can drive consumption patterns that may lead to health issues such as obesity and diabetes.
Why Sugary Foods Are Hard to Resist
Sugary foods are notoriously difficult to resist, and this can be attributed to both their taste and availability. The combination of sugar with fats and additives in many processed foods enhances their flavor, making them incredibly tempting. In fact, the sensory appeal of these products can trigger the brain’s reward system, releasing dopamine and leading to feelings of pleasure and satisfaction. This response not only reinforces the desire for more sugary foods but also contributes to repeated cycles of cravings and consumption.
With the average American consuming nearly 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, it’s clear that these tasty yet unhealthy options are a staple in many diets. This high level of added sugar consumption raises concerns about long-term health consequences, encouraging some to seek alternatives. Such awareness can lead individuals to read labels and make more informed dietary choices, ultimately reducing their sugar intake to a healthier level that aligns with the recommendations from health organizations.
The Impact of Processed Foods on Sugar Cravings
The rise of processed foods in the market has had a significant impact on sugar cravings. Many of these foods are engineered to be hyper-palatable, meaning they are designed specifically to appeal to our taste buds, often through the addition of sugar, fat, and salt. Such combinations create products that are difficult to resist, leading to increased sugar cravings and higher overall consumption. This trend not only contributes to individual health issues but also poses a larger public health challenge as dietary habits become entrenched.
By understanding the connection between processed foods and sugar cravings, individuals can better navigate their dietary choices. Incorporating more whole foods into their diet can help mitigate cravings for processed sugar-laden foods. Fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provide natural sugars that are accompanied by fiber and other nutrients, promoting better health and reducing the likelihood of consuming high amounts of added sugars.
Healthy Ways to Manage Sugar Intake
Managing sugar intake effectively involves several practical strategies that can help individuals enjoy sweetness in their diets without overindulging. Gradually reducing added sugar consumption rather than eliminating it entirely can help minimize withdrawal symptoms and cravings. Instead of going cold turkey, substituting sugary snacks with healthier alternatives, such as fruits, can satisfy sweet cravings while providing essential nutrients.
Another important approach is to read food labels carefully and become aware of the sugar content in products. Many foods that seem healthy might contain hidden added sugars. By choosing items with lower added sugar levels and focusing on whole foods, individuals can enjoy a balanced diet that includes necessary nutrients while still catering to their sweet tooth in a controlled manner.
The Role of Sugar in a Balanced Diet
Sugar, in moderation, can play a role in a balanced diet. It is important to distinguish between naturally occurring sugars found in fruits, vegetables, and dairy products and added sugars present in processed foods. While natural sugars offer nutritional benefits along with fiber, vitamins, and minerals, added sugars provide empty calories with little to no nutritional value. Therefore, it is essential to focus on minimizing the consumption of added sugars while allowing for small amounts of natural sugars to enhance flavor without compromising health.
Incorporating a sensible amount of naturally sweet foods can also promote overall well-being and satisfaction. Encouraging a diet that includes fruits and whole grains can allow for a sweet flavor profile while maintaining nutritional integrity. Ultimately, embracing a more holistic view of sugar as part of a healthy lifestyle can help alleviate concerns about sugar addiction while promoting informed dietary choices.
Understanding Sugar Cravings
Understanding sugar cravings is critical for those looking to manage their intake effectively. These cravings can often stem from emotional triggers, stress, or simply the body’s need for quick energy. When individuals experience low energy levels or mood dips, they might instinctively reach for sugary snacks, perceiving them as a quick fix. This association between sugar and an instant boost can create a cycle of reaching for sweet foods whenever energy is low.
In addition, certain habits and routines can also reinforce sugar cravings. For example, consuming sugary foods at specific times, such as during a break at work or as a reward after a long day, can create habitual patterns that the brain associates with pleasure and satisfaction. Recognizing these patterns can help individuals break the cycle of cravings and develop healthier alternatives to fulfill their emotional and physical needs.
Long-term Effects of Excessive Sugar Consumption
Excessive sugar consumption can lead to a myriad of long-term health effects, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and even heart disease. The relationship between added sugar and these health issues has become one of the focal points of nutritional research. Studies have shown that high sugar intake can lead to insulin resistance, weight gain, and alterations in fat metabolism, creating a domino effect that significantly increases the risk of developing serious health conditions.
Beyond physical health, there are also psychological effects associated with high sugar consumption. The reliance on sugar for a mood boost can create a vicious cycle, leading to more cravings and potential emotional dependence on sugary foods. Being aware of these long-term effects is crucial for individuals looking to optimize their health through better dietary choices and understanding the implications of sugar on overall well-being.
Sugar in the Modern Diet
Sugar continues to be a prominent feature in the modern diet, largely due to the proliferation of processed foods laden with added sugars. The convenience and availability of these foods result in elevated sugar consumption among individuals, often without their knowledge. It’s important to address the culture surrounding sugar in our diets and recognize the impact of marketing and food production practices that contribute to high levels of added sugar in everyday products.
As society becomes more aware of the health implications of excessive sugar consumption, efforts are being made to reformulate products, promote better labeling practices, and educate the public on healthier eating. Advocating for increased health literacy regarding sugar consumption can empower individuals to make informed dietary choices, reducing reliance on unhealthy sugary products in favor of more nutritious options.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like other substances such as alcohol or nicotine?
While sugar can heighten cravings and promote compulsive eating behaviors, it is not officially classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. Research indicates that although people may experience withdrawal-like symptoms when they stop consuming sugar, these are generally less severe than those associated with true addictive substances.
What are the effects of sugar addiction in daily life?
The effects of what some may refer to as sugar addiction include increased cravings for sugary foods and beverages, leading to habitual consumption of ultra-processed products. This can result in health issues such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease, highlighting the importance of moderating added sugar consumption.
How do sugar cravings develop in individuals?
Sugar cravings typically develop due to the consumption of highly palatable foods that contain added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium. These foods are designed to be delicious and convenient, leading to habitual eating. When individuals try to cut back on sugar, they may experience withdrawal symptoms akin to those experienced with addictive substances.
What role do added sugars play in food addiction?
Added sugars contribute to the addictive qualities of certain foods by enhancing their taste and palatability. This can lead to overconsumption, habitual eating patterns, and an increased risk of health issues. Thus, being mindful of added sugar consumption is crucial for maintaining a balanced diet.
How much sugar is considered safe to consume daily?
The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar consumption to a maximum of 9 teaspoons for men, 6 teaspoons for women, and even less for children. Most Americans currently exceed these recommendations, largely due to the consumption of sugary beverages and snacks.
Can reducing sugar consumption be effective for overcoming sugar cravings?
Gradually reducing added sugar intake, rather than stopping abruptly, can be an effective strategy for managing sugar cravings. This approach can help minimize withdrawal-like symptoms and make it easier to transition to a healthier diet while still enjoying some sweetness.
What is the importance of moderating sugar intake in a diet?
Moderating sugar intake is essential as excessive consumption of added sugars is linked to various health problems, such as obesity and heart disease. A balanced approach, where low to moderate amounts of sugar are included, can enhance flavor and pleasure without significant health risks.
Is sugar present in natural foods considered harmful?
No, sugar found in natural foods like fruits, vegetables, and dairy is not considered harmful in moderation. These foods provide essential nutrients, and the sugars they contain are accompanied by fiber and other beneficial compounds. The focus should be on reducing added sugars, which are often found in processed foods.
What strategies can help with managing sugar cravings effectively?
To manage sugar cravings effectively, consider strategies such as gradually reducing added sugar intake, reading food labels to become aware of sugar content, and choosing whole foods that naturally contain sugars. Incorporating a balanced diet rich in nutrients can also help satisfy cravings without resorting to excessive sugar consumption.
What is the difference between sugar and addictive substances?
The key difference between sugar and addictive substances like alcohol or nicotine is the classification of addiction. While sugar can enhance cravings and exhibit some addictive qualities, it is regarded as a necessary nutrient in our diets, unlike substances that can be entirely eliminated.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Cravings for Sugar | Cravings for sugar are real, supported by research, although comparing sugar to addictive substances like alcohol and nicotine is controversial. |
| Addiction Classification | While sugar can induce cravings, it does not meet the strict clinical criteria for addiction like alcohol or nicotine. |
| Sugar in Our Diet | Sugar is necessary in moderation for our diet; it is naturally found in fruits and dairy products. |
| Impact of Ultra-Processed Foods | Ultra-processed foods with high sugar content raise cravings and can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms when reduced abruptly. |
| Recommended Sugar Intake | The American Heart Association recommends limited sugar intake: 9 tsp for men, 6 for women, and less for children. |
| Gradual Reduction | To cut back on sugar, gradually reducing intake is more effective than stopping abruptly. |
Summary
Is Sugar Addictive? This question has generated significant debate in nutritional science. While research indicates that sugar can lead to cravings and compulsive behaviors, it does not fit the clinical definition of an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. Moreover, sugar is a natural part of our diet, found in many healthy foods, suggesting that while it may have addictive qualities, it is vital for maintaining a balanced diet. Moderation is key, as excessive consumption can lead to withdrawal symptoms similar to those seen with more severe addictions. Educating ourselves about sugar intake and recognizing the content in food labels can help maintain a healthy lifestyle.